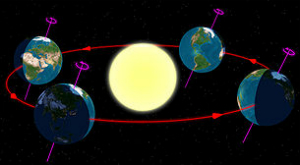
Diagram of the Earth’s seasons as seen from the north. Far right: December solstice
The Summer Solstice occurs exactly when the Earth’s axial tilt is most inclined towards the sun at its maximum of 23° 26′. Though the Summer Solstice is an instant in time, the term is also colloquially used like Midsummer to refer to the day on which it occurs. Except in the polar regions (where daylight is continuous for many months during the spring and summer), the day on which the Summer Solstice occurs is the day of the year with the longest period of daylight. Thus the seasonal significance of the Summer Solstice is in the reversal of the gradual shortening of nights and lengthening of days. The summer solstice occurs in June in the Northern Hemisphere, in December in the Southern Hemisphere.
Continue reading Summer Solstice


